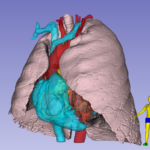
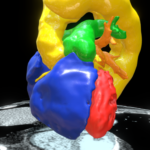
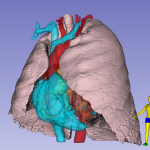
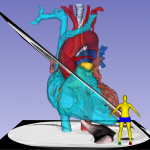
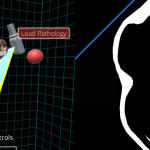
Interactive rendering of lung and heart blood pools
for teaching TTE
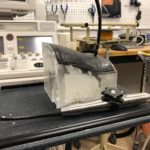
Cast Heart for
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite.
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.
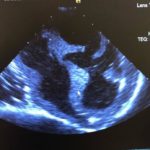
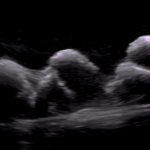
Ultrasound Image from
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.
Customized Procedural Phantoms from 3D Medical Images:
Curriculum-driven, High-fidelity, in-situ Procedural Simulation
“Time for learning curves on patients has passed.” Yet most first procedures are still performed on patients.
3D image processing and micromanufacturing systems now allow development of high-fidelity phantoms based on real anatomy
- Tailored to specific curriculum and educational objectives.
- Wide range of normal and pathologic variants based on real cases.
- Low-cost and repairable – high wear parts easily replaced or refreshed.
- Accessible in large numbers for group teaching and deployments across distributed teaching sites.
- Open-source collaboration and sharing of designs and anatomic atlases across academic centers.
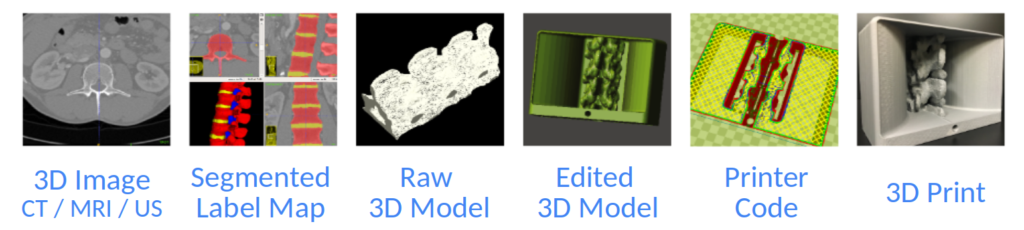
From Medical Image to Phantom: Workflows
CT Data. Segmented with ITK-Snap. Raw 3D model exported as triangle mesh in STL format. Enclosure created in OpenSCAD. Final mesh file converted to printer code (g-code) by Slic3r and printed using FDM with PETG.Thecal sac made using silicone tubing. Ligamentum flavum simulated with dense silicone. Soft tissue ballistic gel. Needle holes can be treated with heat-gun.
Echocardiography Simulator & Anatomical Teaching Models

Everything illustrated here was derived from a single Cardiac CT. The digital 3D models derived from the CT have been used to create renderings, animations, 3D prints of the myocardium, and blood pools, interactive rendering of all structures and three simulators: web-based, virtual-reality and physical echogenic phantom produced using 3D printing and gel casting techniques. See also: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2020.07.008
Our Approach: curriculum-based Technology Development
Ideally simulators are developed as part of a need-driven curriculum (“Nail-First Approach”)
- Identify task elements and steps and corresponding learning objectives
- Set-Up; Positioning; Landmarking; Ultrasound Anatomy; Eye-Hand-Needle Coordination; Tactile Feedback
- Identify learning stages and organize objectives by stage
- Identify type (tactile, visual, ultrasound) & optimal level of fidelity required for each stage
- Live tissue is not always the gold standard!
- Identify required interactions & best modalities for each stage:
- 2D, 3D print / Render / VR / AR / Banana / Chicken
- Cost, Accessibility, Usability, Interactions, Storage
Gallery

Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.

Augmented Reality (AR)
projection of heart and ribcage on echocardiography phantom.
Cardiac CT.
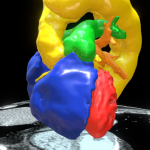
Interactive rendering
Toronto Heart Atlas
Normal Morphology; Type-A Aortic Dissection

Ultrasound-guided subclavian central venous access task trainer
CT data. FDM printing. Silicone and gel casting. Lasercut case.
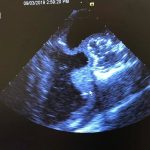
Ultrasound Image from
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.
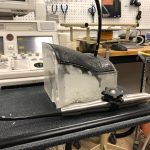
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.
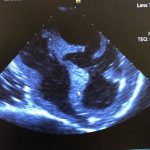
Ultrasound Image from
Echocardiography phantom
CT data. FDM printed positives, Silicone molds; Gel wax and ballistic gel casts with graphite. Lasercut case.

Toronto Heart Atlas
Complex TGA; Situs inversus; Dextrocardia. Post insertion of RV to PA conduit.
Cardiac CT. FDM Print.
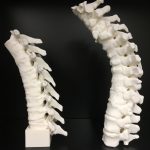
Spine models
for development of neuraxial anesthesia phantom
CT. FDM Print.

Ultrasound-guided vascular access phantom
CAD. FDM printing. Gel casting. Lasercut case.

Ultrasound-guided subclavian central venous access task trainer
CT data. FDM printing. Silicone and gel casting. Lasercut case.

Lung-isolation Training Phantom
CT. FDM print.

Thoracic epidural insertion
CT. Educational Animation.

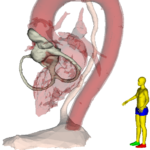
TEE simulator controller
Using 2-button wheel-mouse simulates change of probe depth, omniplane angle and probe flexion.

Spine models
for development of neuraxial anesthesia phantom
CT. FDM Print.

Spine model - Scoliosis
for development of neuraxial anesthesia phantom
CT. FDM Print.

FOCUS Heart Models
showing standard imaging planes for FOCUS TTE
Cardiac CT. FDM Print. Magnets

TEE simulator controller
Using 2-button wheel-mouse simulates change of probe depth, omniplane angle and probe flexion.